Current pharmacological treatments contribute little to the quality of life of people with dementia. They need to be complemented by non-pharmacological interventions which have a potential of improving or maintaining quality of life by:
- reinforcing or stabilising functional ability
- compensating difficulties
- reducing barriers
- enhancing communication
- reducing behavioural problems
- providing a safe and supportive environment
- ensuring physical, psychological, and spiritual well-being.
It is important to note that the symptoms of dementia, particularly changed behaviours (e.g., apathy, agitation, irritability, hyperactivity) are often caused by unmet needs, inappropriate communication styles, loneliness, and boredom – i. e. by causes which are modifiable.
Which kinds of non-pharmacological interventions are available?
Six major forms of non-pharmacological interventions may be distinguished according to their respective targets and strategies.
1. Cognition-focused interventions
| Cognitive stimulation | Engagement in a range of activities and discussions, usually in the form of group sessions led by a trained coordinator and aimed at general enhancement of cognitive and social functioning. |
| Cognitive training | Guided practice on a set of tasks targeting specific cognitive functions such as memory, information processing speed, or visuospatial ability. Cognitive training may include learning of memory strategies (mnemonics) and can be offered in individual or group sessions. |
| Reminiscence therapy | Recall of events in a person’s life; it typically involves weekly group meetings in which participants are encouraged to talk about past events, often assisted by aids such as photos, music or household objects. „Life books“ are individual collections of important events using traditional or electronic media. |
| Speech and language therapy | Training of speech and language skills to improve verbal and nonverbal communication. |
2. Function-focused interventions
| Cognitive rehabilitation | An individualised approach where personally relevant goals are identified, and the therapist works with the person and their family to develop strategies for attaining these goals, development and implementation of compensatory strategies is a key feature. |
| Occupational therapy | Addresses basic and complex activities of daily living; education, work, and household chores, play and leisure, and social participation. Occupational therapists support people in staying active and independent, regarding home maintenance, food preparation shopping, mobility, financial management and communication. Occupational therapy may take advantage of assistive technology devices. |
| Assistive technology | Goals are to maintain a healthy and safe environment, enable people with dementia to live independently, reduce stress and burden of informal caregivers, keep people with dementia cognitively fit, improve their quality of life and postpone institutionalisation. Types of technology for people with dementia include safety devices, memory aids, social and interaction tools, everyday task-supporting devices, leisure activity-supporting tools and training programs for professionals. Virtual reality and augmented reality is an important evolving field. |
| Environmental modification | Dementia-friendly design and adaptations in the physical environment may involve lighting, walking surfaces, stairs, seating, familiarity of setting, arrangement of objects, sound management and cues supporting orientation. |

3. Behaviour-focused interventions
| Behaviour modification | Modification of circumstances or events that trigger the target behaviour, reinforcement of desired behaviour, establishment of behavioural routines, relaxation techniques and teaching of communication skills. |
| Cognitive-behavioural therapy | This technique is used to reduce depression and anxiety in people with dementia. The focus is not on modifying dysfunctional thoughts but on introducing meaningful and pleasurable activities. |
4. Emotion-focused interventions
| Music therapy, dance therapy, arts therapy | Listening to or playing music; creative activities Empathy, acknowledgment of subjective views of people with dementia Using essential oils for promoting relaxation and sleep; addressing the senses by lighting, colours, touch, scents, and sounds. |
| Validation | Empathy, acknowledgment of subjective views of people with dementia |
| Aroma therapy, multi-sensory stimulation | Using essential oils for promoting relaxation and sleep; addressing the senses by lighting, colours, touch, scents, and sounds. |
5. Physical-focused interventions
| Physical exercise | Exercises must be adjusted to the physical capacity of the person with dementia. The goal is five times 30-45 minutes of moderate activity involving exercises for endurance, strength, flexibility and balance. |
6. Carer-focused interventions
| Carer support groups | They aim at improving carers’ ability to cope with dementia. Usually, such programs combine information about dementia with practical problem solving, particularly with regard to changed behaviours, stress management, legal as well as financial advice. |
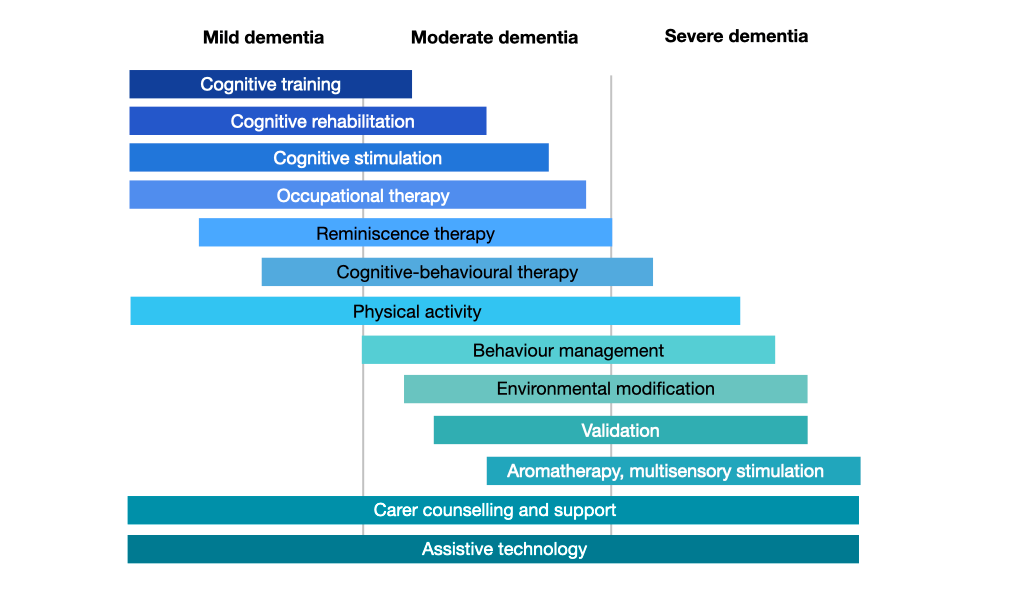
At which stage of dementia should non-pharmacological interventions be used?
The various types of non-pharmacological interventions are most appropriate at specific stages of dementia. At the stage of mild dementia, interventions that target cognition and activities are most helpful. At the stage of moderate dementia, interventions that focus on behaviour are indicated. At the stage of severe dementia, non-pharmacological treatments that try to improve wellbeing are needed. Physical activity, assistive technologies and carer-focused interventions are essential at all stages.
Efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions
Cognition-focused interventions
Cognitive stimulation
Cognitive stimulation programmes benefit cognition in people with mild to moderate dementia over and above any medication effects. This benefit is maintained up to three months after the end of treatment. Cognitive stimulation also provides improvements in self-reported quality of life and well-being, and on staff ratings of communication and social interaction. It had no effects on mood, activities of daily living, changed behaviours or family caregiver outcomes. Computer-based forms of cognitive stimulation have been found to be as effective as traditional formats.
Cognitive training
In people with mild cognitive impairment, computer-based cognitive training produces small to moderate effects on global cognition, attention, and memory. In people with dementia, there are only weak effects on overall cognitive ability. The lack of demonstrable significant benefits derived from cognitive training may be due to methodological issues. Particularly, some gains may not be captured by the available outcome measures.
Reminiscence therapy
In people with dementia reminiscence therapy has a small effect on cognitive functions and a moderate effect on depressive symptoms.
Speech and language therapy
People with the language variants of frontotemporal dementia (primary non-fluent aphasia, semantic dementia) may benefit from speech therapy to help them adjust to their language difficulties and adopt alternative ways to communicate. In people with primary non-fluent aphasia 11 months of weekly speech therapy over 11 helps preserving naming ability.
Function-focused interventions
Cognitive rehabilitation
In people with mild to moderate dementia eight individual sessions of cognitive rehabilitation delivered by a specially trained occupational therapist in the participants’ homes provides significant improvements regarding performance on pre-defined personally relevant goals.
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy has positive effects on activities of daily living and quality of life of people with dementia while also improving carers’ skills. In residential care, providing individually tailored meaningful activities to people with dementia reduces problem behaviours.
Assistive technology
Only few evaluation studies have included people with dementia. Most studies have tested devices that support day-to-day living activities, safety monitoring and health care. These include locator devices, automatic medication dispensers, automatic lighting, simplified mobile phones and television remote controls. Night monitoring devices (bed exit alarms, alarm systems, tracking devices, automatic nightlights, bracelets with teleassistance) reduce the incidence of falls and unattended exits at home. More sophisticated devices can be confusing and irritating for people with impaired cognition.
Environmental modification
Removing unnecessary objects, simplifying the environment, labelling objects, the use of colour contrast and purposeful placement of objects reduces the amount of help needed to perform activities of daily living and fosters independence. Noise reduction can decrease undesired behaviours. A homelike dining atmosphere and a help-yourself layout increases food intake and increases communication. Arrows and signs with the word „toilet“ and a picture can be effective in directing people with dementia to enter and use the toilet independently.
Behaviour-focused interventions
Behaviour management
Behaviour management can reduce problem behaviours, enhance caregivers’ confidence in managing the behaviour, and improve caregivers’ emotional wellbeing and subjective burden. Strategies that have been positively evaluated in people with behavioural-variant Frontotemporal dementia include simplifying social situations, reducing noise and stimulation, removing access to critical items (e. g. credit cards), modifying public outings, appropriate cueing, introducing old hobbies and games, occupational therapy, and music therapy.
Cognitive-behavioural therapy
This form of psychological treatment reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety in people with dementia.
Emotion-focused interventions
Music therapy
In people with dementia music therapy reduces depression, enhances social interaction, ameliorates problem behaviours, and maintains perceptual-motor skills. Music therapy can also improve depressive symptoms and alleviate anxiety and stress.
Aroma therapy
In people with dementia, aromatherapy is used to reduce problem behaviours, enhance sleep, and stimulate motivation.
Validation
Some studies have demonstrated a reduction of problem behaviours and depressive symptoms. There were no effects on cognitive ability or activities of daily living.
Multi-sensory stimulation
Multi-sensory stimulation has positive effects on problem behaviours and mood during and immediately after the sessions. Long-term benefits and generalisation to other environments as well as effects on cognition and functional ability are questionable.
Physical-focused interventions
Physical exercise improves participants’ physical fitness and is associated with reduced caregiver burden due to problem behaviours. Physical activity also has a significant effect on the ability of people with dementia to perform activities of daily living.
Carer-focused interventions
Participation in support groups led by professionals improves caregivers’ mood and reduces burden. These effects last up to 3 months after program termination. Educating caregivers in behaviour modification techniques can reduce problem behaviours in people with dementia. Factors that are associated with the success of caregiver groups include theoretical foundation of the intervention, active role of participants, room for individual problems and focus on the management of problem behaviours.
Non-pharmacological interventions in the course of dementia